Learning hierarchical behavior and motion planning for autonomous driving
Learning-based driving solution, a new branch for autonomous driving, is expected to simplify the modeling of driving by learning the underlying mechanisms from data. To improve the tactical decision-making for learning-based driving solution, we introduce hierarchical behavior and motion planning (HBMP) to explicitly model the behavior in learning-based solution. Due to the coupled action space of behavior and motion, it is challenging to solve HBMP problem using reinforcement learning (RL) for long-horizon driving tasks. We transform HBMP problem by integrating a classical sampling-based motion planner, of which the optimal cost is regarded as the rewards for high-level behavior learning. As a result, this formulation reduces action space and diversifies the rewards without losing the optimality of HBMP. In addition, we propose a sharable representation for input sensory data across simulation platforms and real-world environment, so that models trained in a fast event-based simulator, SUMO, can be used to initialize and accelerate the RL training in a dynamics based simulator, CARLA. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method. Besides, the model is successfully transferred to the real-world, validating the generalization capability.
PDF Abstract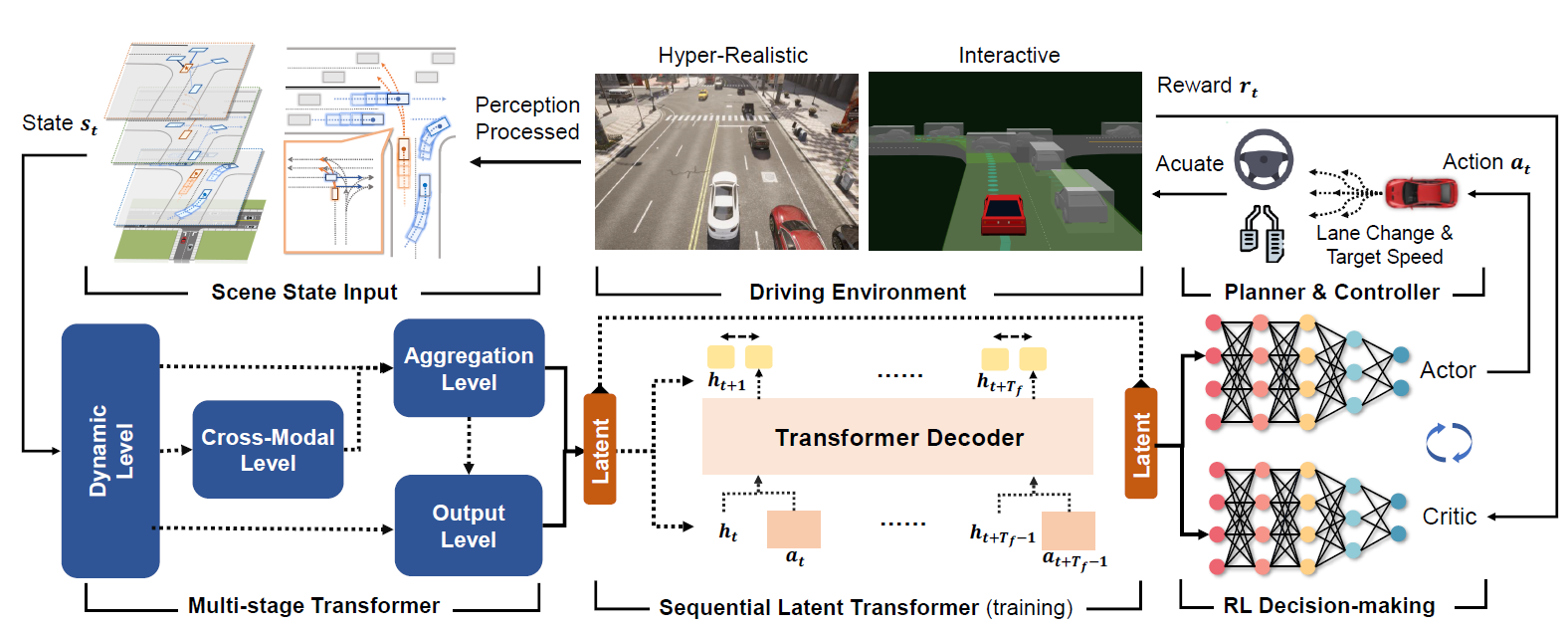




 CARLA
CARLA