Self-Supervised Learning of Object Parts for Semantic Segmentation
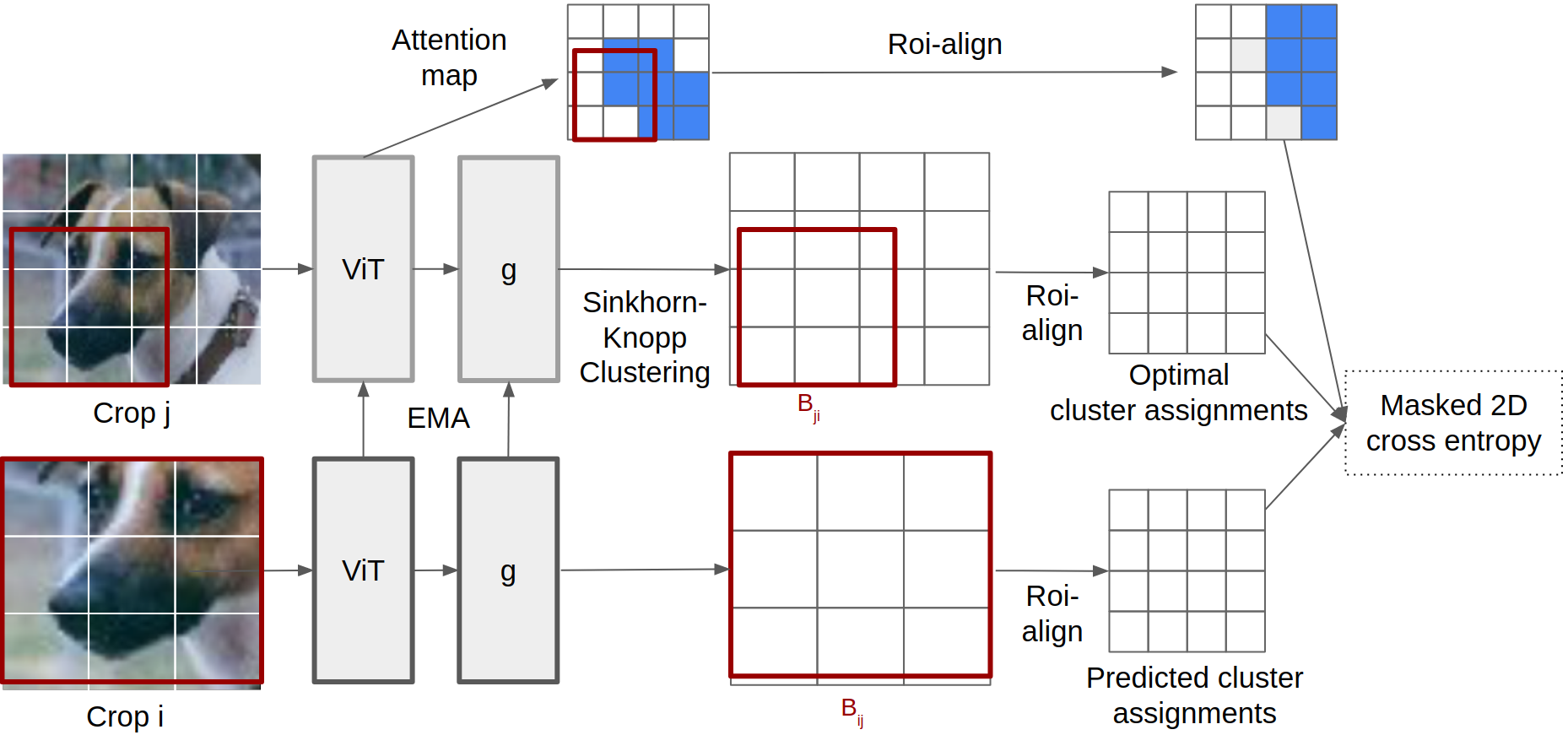
Progress in self-supervised learning has brought strong general image representation learning methods. Yet so far, it has mostly focused on image-level learning. In turn, tasks such as unsupervised image segmentation have not benefited from this trend as they require spatially-diverse representations. However, learning dense representations is challenging, as in the unsupervised context it is not clear how to guide the model to learn representations that correspond to various potential object categories. In this paper, we argue that self-supervised learning of object parts is a solution to this issue. Object parts are generalizable: they are a priori independent of an object definition, but can be grouped to form objects a posteriori. To this end, we leverage the recently proposed Vision Transformer's capability of attending to objects and combine it with a spatially dense clustering task for fine-tuning the spatial tokens. Our method surpasses the state-of-the-art on three semantic segmentation benchmarks by 17%-3%, showing that our representations are versatile under various object definitions. Finally, we extend this to fully unsupervised segmentation - which refrains completely from using label information even at test-time - and demonstrate that a simple method for automatically merging discovered object parts based on community detection yields substantial gains.
PDF Abstract CVPR 2022 PDF CVPR 2022 AbstractCode
Datasets
Results from the Paper
 Ranked #5 on
Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
on PASCAL VOC 2012 val
(using extra training data)
Ranked #5 on
Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
on PASCAL VOC 2012 val
(using extra training data)








 MS COCO
MS COCO