Unsupervised Brain Tumor Segmentation with Image-based Prompts
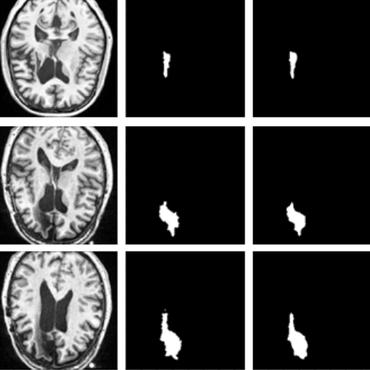
Automated brain tumor segmentation based on deep learning (DL) has achieved promising performance. However, it generally relies on annotated images for model training, which is not always feasible in clinical settings. Therefore, the development of unsupervised DL-based brain tumor segmentation approaches without expert annotations is desired. Motivated by the success of prompt learning (PL) in natural language processing, we propose an approach to unsupervised brain tumor segmentation by designing image-based prompts that allow indication of brain tumors, and this approach is dubbed as PL-based Brain Tumor Segmentation (PL-BTS). Specifically, instead of directly training a model for brain tumor segmentation with a large amount of annotated data, we seek to train a model that can answer the question: is a voxel in the input image associated with tumor-like hyper-/hypo-intensity? Such a model can be trained by artificially generating tumor-like hyper-/hypo-intensity on images without tumors with hand-crafted designs. Since the hand-crafted designs may be too simplistic to represent all kinds of real tumors, the trained model may overfit the simplistic hand-crafted task rather than actually answer the question of abnormality. To address this problem, we propose the use of a validation task, where we generate a different hand-crafted task to monitor overfitting. In addition, we propose PL-BTS+ that further improves PL-BTS by exploiting unannotated images with brain tumors. Compared with competing unsupervised methods, the proposed method has achieved marked improvements on both public and in-house datasets, and we have also demonstrated its possible extension to other brain lesion segmentation tasks.
PDF Abstract