NoMIRACL: Knowing When You Don't Know for Robust Multilingual Retrieval-Augmented Generation
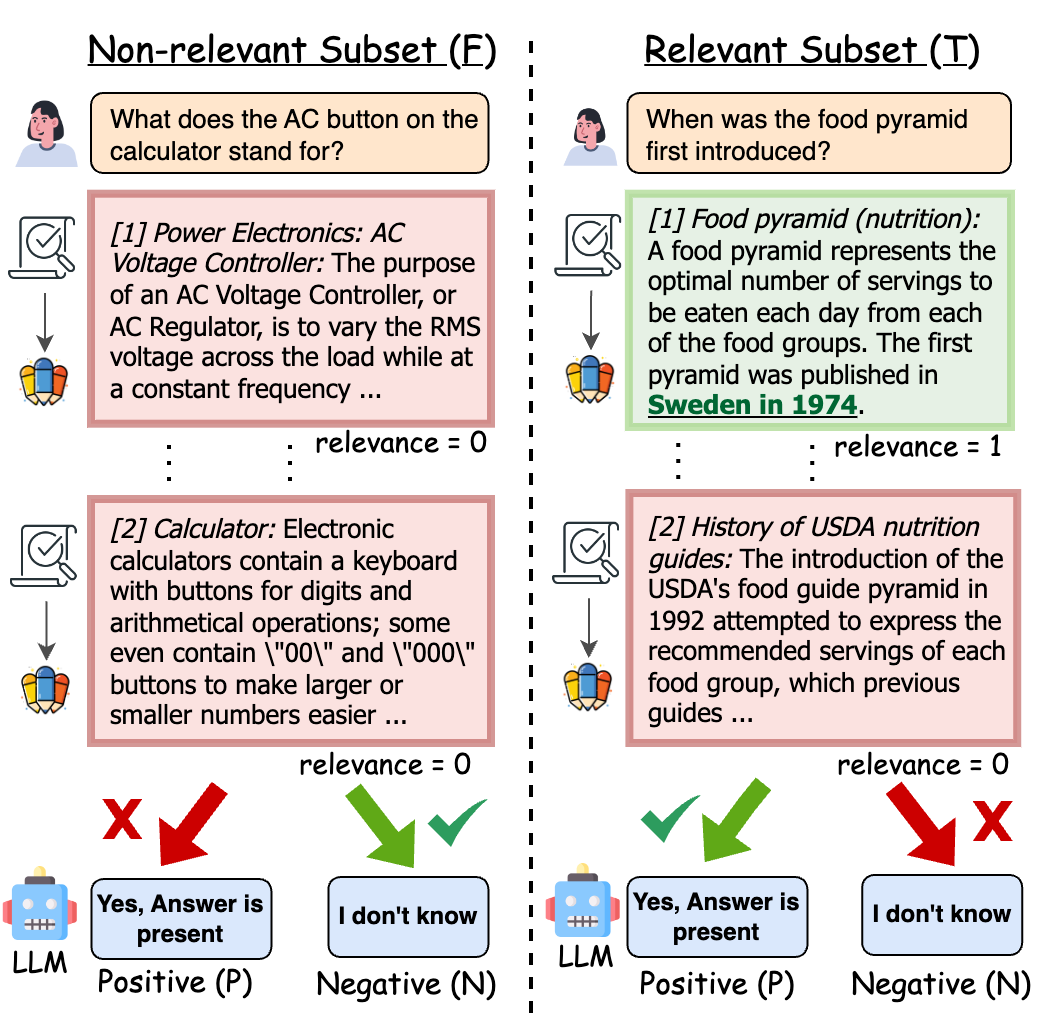
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) grounds large language model (LLM) output by leveraging external knowledge sources to reduce factual hallucinations. However, prior works lack a comprehensive evaluation of different language families, making it challenging to evaluate LLM robustness against errors in external retrieved knowledge. To overcome this, we establish NoMIRACL, a human-annotated dataset for evaluating LLM robustness in RAG across 18 typologically diverse languages. NoMIRACL includes both a non-relevant and a relevant subset. Queries in the non-relevant subset contain passages judged as non-relevant, whereas queries in the relevant subset include at least a single judged relevant passage. We measure LLM robustness using two metrics: (i) hallucination rate, measuring model tendency to hallucinate an answer, when the answer is not present in passages in the non-relevant subset, and (ii) error rate, measuring model inaccuracy to recognize relevant passages in the relevant subset. In our work, we measure robustness for a wide variety of multilingual-focused LLMs and observe that most of the models struggle to balance the two capacities. Models such as LLAMA-2, Orca-2, and FLAN-T5 observe more than an 88% hallucination rate on the non-relevant subset, whereas, Mistral overall hallucinates less, but can achieve up to a 74.9% error rate on the relevant subset. Overall, GPT-4 is observed to provide the best tradeoff on both subsets, highlighting future work necessary to improve LLM robustness.
PDF Abstract