GaitMixer: Skeleton-based Gait Representation Learning via Wide-spectrum Multi-axial Mixer
Most existing gait recognition methods are appearance-based, which rely on the silhouettes extracted from the video data of human walking activities. The less-investigated skeleton-based gait recognition methods directly learn the gait dynamics from 2D/3D human skeleton sequences, which are theoretically more robust solutions in the presence of appearance changes caused by clothes, hairstyles, and carrying objects. However, the performance of skeleton-based solutions is still largely behind the appearance-based ones. This paper aims to close such performance gap by proposing a novel network model, GaitMixer, to learn more discriminative gait representation from skeleton sequence data. In particular, GaitMixer follows a heterogeneous multi-axial mixer architecture, which exploits the spatial self-attention mixer followed by the temporal large-kernel convolution mixer to learn rich multi-frequency signals in the gait feature maps. Experiments on the widely used gait database, CASIA-B, demonstrate that GaitMixer outperforms the previous SOTA skeleton-based methods by a large margin while achieving a competitive performance compared with the representative appearance-based solutions. Code will be available at https://github.com/exitudio/gaitmixer
PDF Abstract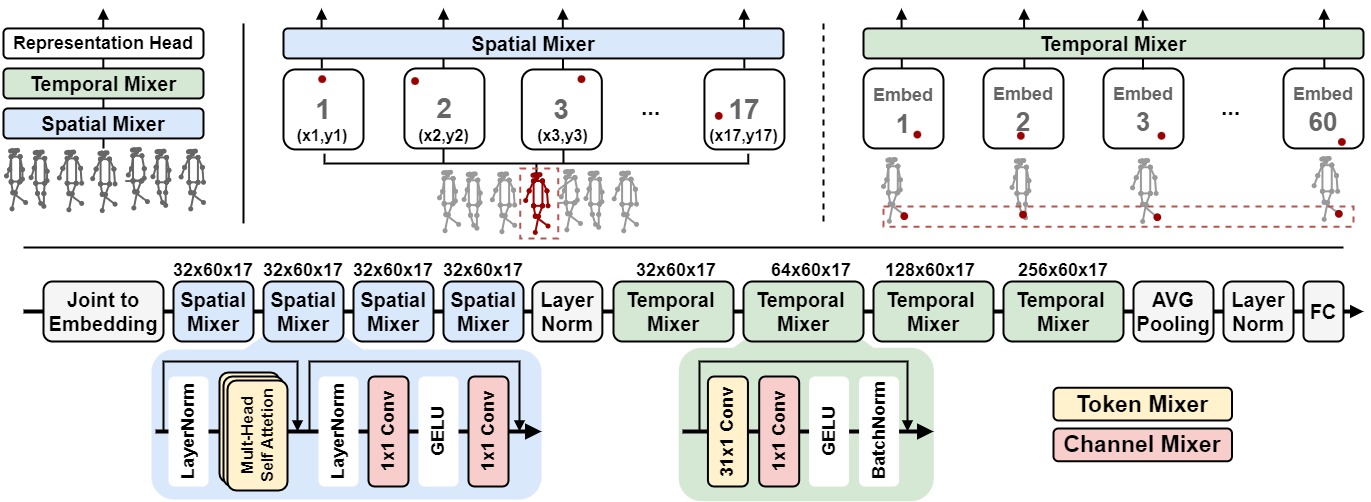





 CASIA-B
CASIA-B
