Search Results for author: Hatice Gunes
Found 28 papers, 11 papers with code
Federated Learning of Socially Appropriate Agent Behaviours in Simulated Home Environments
1 code implementation • 12 Mar 2024 • Saksham Checker, Nikhil Churamani, Hatice Gunes
In this paper, we present a novel FL benchmark that evaluates different strategies, using multi-label regression objectives, where each client individually learns to predict the social appropriateness of different robot actions while also sharing their learning with others.
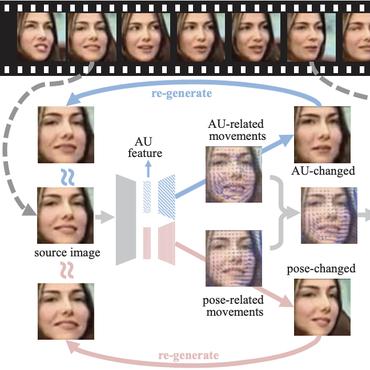
REACT 2024: the Second Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation Challenge
1 code implementation • 10 Jan 2024 • Siyang Song, Micol Spitale, Cheng Luo, Cristina Palmero, German Barquero, Hengde Zhu, Sergio Escalera, Michel Valstar, Tobias Baur, Fabien Ringeval, Elisabeth Andre, Hatice Gunes
In dyadic interactions, humans communicate their intentions and state of mind using verbal and non-verbal cues, where multiple different facial reactions might be appropriate in response to a specific speaker behaviour.
Uncertainty-based Fairness Measures
no code implementations • 18 Dec 2023 • Selim Kuzucu, Jiaee Cheong, Hatice Gunes, Sinan Kalkan
Unfair predictions of machine learning (ML) models impede their broad acceptance in real-world settings.
MRecGen: Multimodal Appropriate Reaction Generator
no code implementations • 5 Jul 2023 • Jiaqi Xu, Cheng Luo, Weicheng Xie, Linlin Shen, Xiaofeng Liu, Lu Liu, Hatice Gunes, Siyang Song
Verbal and non-verbal human reaction generation is a challenging task, as different reactions could be appropriate for responding to the same behaviour.
REACT2023: the first Multi-modal Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation Challenge
1 code implementation • 11 Jun 2023 • Siyang Song, Micol Spitale, Cheng Luo, German Barquero, Cristina Palmero, Sergio Escalera, Michel Valstar, Tobias Baur, Fabien Ringeval, Elisabeth Andre, Hatice Gunes
The Multi-modal Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation Challenge (REACT2023) is the first competition event focused on evaluating multimedia processing and machine learning techniques for generating human-appropriate facial reactions in various dyadic interaction scenarios, with all participants competing strictly under the same conditions.
ReactFace: Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation in Dyadic Interactions
1 code implementation • 25 May 2023 • Cheng Luo, Siyang Song, Weicheng Xie, Micol Spitale, Linlin Shen, Hatice Gunes
ReactFace generates multiple different but appropriate photo-realistic human facial reactions by (i) learning an appropriate facial reaction distribution representing multiple appropriate facial reactions; and (ii) synchronizing the generated facial reactions with the speaker's verbal and non-verbal behaviours at each time stamp, resulting in realistic 2D facial reaction sequences.
Reversible Graph Neural Network-based Reaction Distribution Learning for Multiple Appropriate Facial Reactions Generation
1 code implementation • 24 May 2023 • Tong Xu, Micol Spitale, Hao Tang, Lu Liu, Hatice Gunes, Siyang Song
This means that we approach this problem by considering the generation of a distribution of the listener's appropriate facial reactions instead of multiple different appropriate facial reactions, i. e., 'many' appropriate facial reaction labels are summarised as 'one' distribution label during training.
Continual Facial Expression Recognition: A Benchmark
no code implementations • 10 May 2023 • Nikhil Churamani, Tolga Dimlioglu, German I. Parisi, Hatice Gunes
Understanding human affective behaviour, especially in the dynamics of real-world settings, requires Facial Expression Recognition (FER) models to continuously adapt to individual differences in user expression, contextual attributions, and the environment.
Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation in Dyadic Interaction Settings: What, Why and How?
1 code implementation • 13 Feb 2023 • Siyang Song, Micol Spitale, Yiming Luo, Batuhan Bal, Hatice Gunes
However, none attempted to automatically generate multiple appropriate reactions in the context of dyadic interactions and evaluate the appropriateness of those reactions using objective measures.
GRATIS: Deep Learning Graph Representation with Task-specific Topology and Multi-dimensional Edge Features
1 code implementation • 19 Nov 2022 • Siyang Song, Yuxin Song, Cheng Luo, Zhiyuan Song, Selim Kuzucu, Xi Jia, Zhijiang Guo, Weicheng Xie, Linlin Shen, Hatice Gunes
Our framework is effective, robust and flexible, and is a plug-and-play module that can be combined with different backbones and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to generate a task-specific graph representation from various graph and non-graph data.
An Open-source Benchmark of Deep Learning Models for Audio-visual Apparent and Self-reported Personality Recognition
1 code implementation • 17 Oct 2022 • Rongfan Liao, Siyang Song, Hatice Gunes
Personality determines a wide variety of human daily and working behaviours, and is crucial for understanding human internal and external states.
Automatic Context-Driven Inference of Engagement in HMI: A Survey
no code implementations • 30 Sep 2022 • Hanan Salam, Oya Celiktutan, Hatice Gunes, Mohamed Chetouani
An integral part of seamless human-human communication is engagement, the process by which two or more participants establish, maintain, and end their perceived connection.
Learning Multi-dimensional Edge Feature-based AU Relation Graph for Facial Action Unit Recognition
2 code implementations • 2 May 2022 • Cheng Luo, Siyang Song, Weicheng Xie, Linlin Shen, Hatice Gunes
While the relationship between a pair of AUs can be complex and unique, existing approaches fail to specifically and explicitly represent such cues for each pair of AUs in each facial display.
 Ranked #3 on
Facial Action Unit Detection
on DISFA
Ranked #3 on
Facial Action Unit Detection
on DISFA
Federated Continual Learning for Socially Aware Robotics
no code implementations • 14 Jan 2022 • Luke Guerdan, Hatice Gunes
We show that decentralized learning is a viable alternative to centralized learning in a proof-of-concept Socially-Aware Navigation domain, and demonstrate how Elastic Transfer improves several of the proposed criteria.
The Effect of Model Compression on Fairness in Facial Expression Recognition
no code implementations • 5 Jan 2022 • Samuil Stoychev, Hatice Gunes
To do that, we set up a neural network classifier to perform facial expression recognition and implement several model compression techniques on top of it.
 Facial Expression Recognition
Facial Expression Recognition
 Facial Expression Recognition (FER)
+2
Facial Expression Recognition (FER)
+2
Two-stage Temporal Modelling Framework for Video-based Depression Recognition using Graph Representation
no code implementations • 30 Nov 2021 • Jiaqi Xu, Siyang Song, Keerthy Kusumam, Hatice Gunes, Michel Valstar
The short-term depressive behaviour modelling stage first deep learns depression-related facial behavioural features from multiple short temporal scales, where a Depression Feature Enhancement (DFE) module is proposed to enhance the depression-related clues for all temporal scales and remove non-depression noises.
Inferring User Facial Affect in Work-like Settings
no code implementations • 22 Nov 2021 • Chaudhary Muhammad Aqdus Ilyas, Siyang Song, Hatice Gunes
Unlike the six basic emotions of happiness, sadness, fear, anger, disgust and surprise, modelling and predicting dimensional affect in terms of valence (positivity - negativity) and arousal (intensity) has proven to be more flexible, applicable and useful for naturalistic and real-world settings.
Learning Graph Representation of Person-specific Cognitive Processes from Audio-visual Behaviours for Automatic Personality Recognition
no code implementations • 26 Oct 2021 • Siyang Song, Zilong Shao, Shashank Jaiswal, Linlin Shen, Michel Valstar, Hatice Gunes
This approach builds on two following findings in cognitive science: (i) human cognition partially determines expressed behaviour and is directly linked to true personality traits; and (ii) in dyadic interactions individuals' nonverbal behaviours are influenced by their conversational partner behaviours.
Toward Affective XAI: Facial Affect Analysis for Understanding Explainable Human-AI Interactions
no code implementations • 16 Jun 2021 • Luke Guerdan, Alex Raymond, Hatice Gunes
As machine learning approaches are increasingly used to augment human decision-making, eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) research has explored methods for communicating system behavior to humans.
Domain-Incremental Continual Learning for Mitigating Bias in Facial Expression and Action Unit Recognition
no code implementations • 15 Mar 2021 • Nikhil Churamani, Ozgur Kara, Hatice Gunes
As Facial Expression Recognition (FER) systems become integrated into our daily lives, these systems need to prioritise making fair decisions instead of aiming at higher individual accuracy scores.
Towards Fair Affective Robotics: Continual Learning for Mitigating Bias in Facial Expression and Action Unit Recognition
no code implementations • 15 Mar 2021 • Ozgur Kara, Nikhil Churamani, Hatice Gunes
As affective robots become integral in human life, these agents must be able to fairly evaluate human affective expressions without discriminating against specific demographic groups.
Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Facial Actions using Lifecycle-Aware Capsule Networks
no code implementations • 17 Nov 2020 • Nikhil Churamani, Sinan Kalkan, Hatice Gunes
In real-world interactions, however, facial expressions are usually more subtle and evolve in a temporal manner requiring AU detection models to learn spatial as well as temporal information.
Affect-Driven Modelling of Robot Personality for Collaborative Human-Robot Interactions
no code implementations • 14 Oct 2020 • Nikhil Churamani, Pablo Barros, Hatice Gunes, Stefan Wermter
Collaborative interactions require social robots to adapt to the dynamics of human affective behaviour.
Investigating Bias and Fairness in Facial Expression Recognition
no code implementations • 20 Jul 2020 • Tian Xu, Jennifer White, Sinan Kalkan, Hatice Gunes
Recognition of expressions of emotions and affect from facial images is a well-studied research problem in the fields of affective computing and computer vision with a large number of datasets available containing facial images and corresponding expression labels.
Facial Electromyography-based Adaptive Virtual Reality Gaming for Cognitive Training
no code implementations • 27 Apr 2020 • Lorcan Reidy, Dennis Chan, Charles Nduka, Hatice Gunes
Cognitive training has shown promising results for delivering improvements in human cognition related to attention, problem solving, reading comprehension and information retrieval.
Registration-free Face-SSD: Single shot analysis of smiles, facial attributes, and affect in the wild
no code implementations • 11 Feb 2019 • Youngkyoon Jang, Hatice Gunes, Ioannis Patras
In this paper, we present a novel single shot face-related task analysis method, called Face-SSD, for detecting faces and for performing various face-related (classification/regression) tasks including smile recognition, face attribute prediction and valence-arousal estimation in the wild.
CNN-based Facial Affect Analysis on Mobile Devices
2 code implementations • 23 Jul 2018 • Charlie Hewitt, Hatice Gunes
Our results show that the proposed architectures retain similar performance to the dataset baseline while minimising storage requirements: achieving 58% accuracy for eight-class emotion classification and average RMSE of 0. 39 for valence/arousal prediction.
Human-Computer Interaction
Face Alignment Assisted by Head Pose Estimation
1 code implementation • 11 Jul 2015 • Heng Yang, Wenxuan Mou, Yichi Zhang, Ioannis Patras, Hatice Gunes, Peter Robinson
In this paper we propose a supervised initialization scheme for cascaded face alignment based on explicit head pose estimation.