Search Results for author: Gordon Wetzstein
Found 91 papers, 30 papers with code
Disambiguating Monocular Depth Estimation with a Single Transient
no code implementations • ECCV 2020 • Mark Nishimura, David B. Lindell, Christopher Metzler, Gordon Wetzstein
Monocular depth estimation algorithms successfully predict the relative depth order of objects in a scene.
Make-it-Real: Unleashing Large Multimodal Model's Ability for Painting 3D Objects with Realistic Materials
no code implementations • 25 Apr 2024 • Ye Fang, Zeyi Sun, Tong Wu, Jiaqi Wang, Ziwei Liu, Gordon Wetzstein, Dahua Lin
Physically realistic materials are pivotal in augmenting the realism of 3D assets across various applications and lighting conditions.
Flying with Photons: Rendering Novel Views of Propagating Light
no code implementations • 9 Apr 2024 • Anagh Malik, Noah Juravsky, Ryan Po, Gordon Wetzstein, Kiriakos N. Kutulakos, David B. Lindell
Combined with this dataset, we introduce an efficient neural volume rendering framework based on the transient field.
PhysAvatar: Learning the Physics of Dressed 3D Avatars from Visual Observations
no code implementations • 5 Apr 2024 • Yang Zheng, Qingqing Zhao, Guandao Yang, Wang Yifan, Donglai Xiang, Florian Dubost, Dmitry Lagun, Thabo Beeler, Federico Tombari, Leonidas Guibas, Gordon Wetzstein
This marks a significant advancement towards modeling photorealistic digital humans using physically based inverse rendering with physics in the loop.
CameraCtrl: Enabling Camera Control for Text-to-Video Generation
1 code implementation • 2 Apr 2024 • Hao He, Yinghao Xu, Yuwei Guo, Gordon Wetzstein, Bo Dai, Hongsheng Li, Ceyuan Yang
Controllability plays a crucial role in video generation since it allows users to create desired content.
TC4D: Trajectory-Conditioned Text-to-4D Generation
no code implementations • 26 Mar 2024 • Sherwin Bahmani, Xian Liu, Yifan Wang, Ivan Skorokhodov, Victor Rong, Ziwei Liu, Xihui Liu, Jeong Joon Park, Sergey Tulyakov, Gordon Wetzstein, Andrea Tagliasacchi, David B. Lindell
We learn local deformations that conform to the global trajectory using supervision from a text-to-video model.
GRM: Large Gaussian Reconstruction Model for Efficient 3D Reconstruction and Generation
1 code implementation • 21 Mar 2024 • Yinghao Xu, Zifan Shi, Wang Yifan, Hansheng Chen, Ceyuan Yang, Sida Peng, Yujun Shen, Gordon Wetzstein
We introduce GRM, a large-scale reconstructor capable of recovering a 3D asset from sparse-view images in around 0. 1s.
Generic 3D Diffusion Adapter Using Controlled Multi-View Editing
1 code implementation • 18 Mar 2024 • Hansheng Chen, Ruoxi Shi, Yulin Liu, Bokui Shen, Jiayuan Gu, Gordon Wetzstein, Hao Su, Leonidas Guibas
Open-domain 3D object synthesis has been lagging behind image synthesis due to limited data and higher computational complexity.
Real-time 3D-aware Portrait Editing from a Single Image
no code implementations • 21 Feb 2024 • Qingyan Bai, Zifan Shi, Yinghao Xu, Hao Ouyang, Qiuyu Wang, Ceyuan Yang, Xuan Wang, Gordon Wetzstein, Yujun Shen, Qifeng Chen
This work presents 3DPE, a practical method that can efficiently edit a face image following given prompts, like reference images or text descriptions, in a 3D-aware manner.
GazeGPT: Augmenting Human Capabilities using Gaze-contingent Contextual AI for Smart Eyewear
no code implementations • 30 Jan 2024 • Robert Konrad, Nitish Padmanaban, J. Gabriel Buckmaster, Kevin C. Boyle, Gordon Wetzstein
Multimodal large language models (LMMs) excel in world knowledge and problem-solving abilities.
GPT-4V(ision) is a Human-Aligned Evaluator for Text-to-3D Generation
1 code implementation • 8 Jan 2024 • Tong Wu, Guandao Yang, Zhibing Li, Kai Zhang, Ziwei Liu, Leonidas Guibas, Dahua Lin, Gordon Wetzstein
These metrics lack the flexibility to generalize to different evaluation criteria and might not align well with human preferences.
Scalable 3D Reconstruction From Single Particle X-Ray Diffraction Images Based on Online Machine Learning
no code implementations • 22 Dec 2023 • Jay Shenoy, Axel Levy, Frédéric Poitevin, Gordon Wetzstein
X-ray free-electron lasers (XFELs) offer unique capabilities for measuring the structure and dynamics of biomolecules, helping us understand the basic building blocks of life.
Orthogonal Adaptation for Modular Customization of Diffusion Models
no code implementations • 5 Dec 2023 • Ryan Po, Guandao Yang, Kfir Aberman, Gordon Wetzstein
In this paper, we address a new problem called Modular Customization, with the goal of efficiently merging customized models that were fine-tuned independently for individual concepts.
Generative Rendering: Controllable 4D-Guided Video Generation with 2D Diffusion Models
no code implementations • 3 Dec 2023 • Shengqu Cai, Duygu Ceylan, Matheus Gadelha, Chun-Hao Paul Huang, Tuanfeng Yang Wang, Gordon Wetzstein
Traditional 3D content creation tools empower users to bring their imagination to life by giving them direct control over a scene's geometry, appearance, motion, and camera path.
4D-fy: Text-to-4D Generation Using Hybrid Score Distillation Sampling
no code implementations • 29 Nov 2023 • Sherwin Bahmani, Ivan Skorokhodov, Victor Rong, Gordon Wetzstein, Leonidas Guibas, Peter Wonka, Sergey Tulyakov, Jeong Joon Park, Andrea Tagliasacchi, David B. Lindell
Recent breakthroughs in text-to-4D generation rely on pre-trained text-to-image and text-to-video models to generate dynamic 3D scenes.
Gaussian Shell Maps for Efficient 3D Human Generation
no code implementations • 29 Nov 2023 • Rameen Abdal, Wang Yifan, Zifan Shi, Yinghao Xu, Ryan Po, Zhengfei Kuang, Qifeng Chen, Dit-yan Yeung, Gordon Wetzstein
Instead of rasterizing the shells directly, we sample 3D Gaussians on the shells whose attributes are encoded in the texture features.
Volumetric Reconstruction Resolves Off-Resonance Artifacts in Static and Dynamic PROPELLER MRI
1 code implementation • 22 Nov 2023 • Annesha Ghosh, Gordon Wetzstein, Mert Pilanci, Sara Fridovich-Keil
Off-resonance artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are visual distortions that occur when the actual resonant frequencies of spins within the imaging volume differ from the expected frequencies used to encode spatial information.
DMV3D: Denoising Multi-View Diffusion using 3D Large Reconstruction Model
no code implementations • 15 Nov 2023 • Yinghao Xu, Hao Tan, Fujun Luan, Sai Bi, Peng Wang, Jiahao Li, Zifan Shi, Kalyan Sunkavalli, Gordon Wetzstein, Zexiang Xu, Kai Zhang
We propose \textbf{DMV3D}, a novel 3D generation approach that uses a transformer-based 3D large reconstruction model to denoise multi-view diffusion.
Pose-to-Motion: Cross-Domain Motion Retargeting with Pose Prior
no code implementations • 31 Oct 2023 • Qingqing Zhao, Peizhuo Li, Wang Yifan, Olga Sorkine-Hornung, Gordon Wetzstein
Our experiments show that our method effectively combines the motion features of the source character with the pose features of the target character, and performs robustly with small or noisy pose data sets, ranging from a few artist-created poses to noisy poses estimated directly from images.
State of the Art on Diffusion Models for Visual Computing
no code implementations • 11 Oct 2023 • Ryan Po, Wang Yifan, Vladislav Golyanik, Kfir Aberman, Jonathan T. Barron, Amit H. Bermano, Eric Ryan Chan, Tali Dekel, Aleksander Holynski, Angjoo Kanazawa, C. Karen Liu, Lingjie Liu, Ben Mildenhall, Matthias Nießner, Björn Ommer, Christian Theobalt, Peter Wonka, Gordon Wetzstein
The field of visual computing is rapidly advancing due to the emergence of generative artificial intelligence (AI), which unlocks unprecedented capabilities for the generation, editing, and reconstruction of images, videos, and 3D scenes.
Gradient Descent Provably Solves Nonlinear Tomographic Reconstruction
no code implementations • 6 Oct 2023 • Sara Fridovich-Keil, Fabrizio Valdivia, Gordon Wetzstein, Benjamin Recht, Mahdi Soltanolkotabi
We show that this approach reduces metal artifacts compared to a commercial reconstruction of a human skull with metal dental crowns.
Instant Continual Learning of Neural Radiance Fields
no code implementations • 4 Sep 2023 • Ryan Po, Zhengyang Dong, Alexander W. Bergman, Gordon Wetzstein
Neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have emerged as an effective method for novel-view synthesis and 3D scene reconstruction.
PointOdyssey: A Large-Scale Synthetic Dataset for Long-Term Point Tracking
2 code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Yang Zheng, Adam W. Harley, Bokui Shen, Gordon Wetzstein, Leonidas J. Guibas
Our goal is to advance the state-of-the-art by placing emphasis on long videos with naturalistic motion.
![]() Ranked #1 on
Point Tracking
on TAP-Vid
Ranked #1 on
Point Tracking
on TAP-Vid
Efficient 3D Articulated Human Generation with Layered Surface Volumes
no code implementations • 11 Jul 2023 • Yinghao Xu, Wang Yifan, Alexander W. Bergman, Menglei Chai, Bolei Zhou, Gordon Wetzstein
These layers are rendered using alpha compositing with fast differentiable rasterization, and they can be interpreted as a volumetric representation that allocates its capacity to a manifold of finite thickness around the template.
Articulated 3D Head Avatar Generation using Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
no code implementations • 10 Jul 2023 • Alexander W. Bergman, Wang Yifan, Gordon Wetzstein
Recent work on text-guided 3D object generation has shown great promise in addressing these needs.
Single-Shot Implicit Morphable Faces with Consistent Texture Parameterization
no code implementations • 4 May 2023 • Connor Z. Lin, Koki Nagano, Jan Kautz, Eric R. Chan, Umar Iqbal, Leonidas Guibas, Gordon Wetzstein, Sameh Khamis
To tackle this problem, we propose a novel method for constructing implicit 3D morphable face models that are both generalizable and intuitive for editing.
Learning Controllable Adaptive Simulation for Multi-resolution Physics
1 code implementation • 1 May 2023 • Tailin Wu, Takashi Maruyama, Qingqing Zhao, Gordon Wetzstein, Jure Leskovec
In this work, we introduce Learning controllable Adaptive simulation for Multi-resolution Physics (LAMP) as the first full deep learning-based surrogate model that jointly learns the evolution model and optimizes appropriate spatial resolutions that devote more compute to the highly dynamic regions.
LumiGAN: Unconditional Generation of Relightable 3D Human Faces
no code implementations • 25 Apr 2023 • Boyang Deng, Yifan Wang, Gordon Wetzstein
Unsupervised learning of 3D human faces from unstructured 2D image data is an active research area.
PixelRNN: In-pixel Recurrent Neural Networks for End-to-end-optimized Perception with Neural Sensors
no code implementations • 11 Apr 2023 • Haley M. So, Laurie Bose, Piotr Dudek, Gordon Wetzstein
Conventional image sensors digitize high-resolution images at fast frame rates, producing a large amount of data that needs to be transmitted off the sensor for further processing.
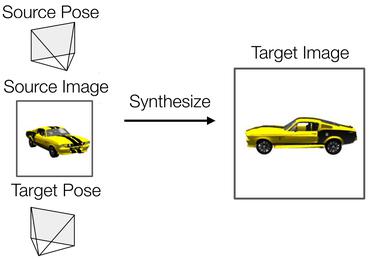
Generative Novel View Synthesis with 3D-Aware Diffusion Models
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Eric R. Chan, Koki Nagano, Matthew A. Chan, Alexander W. Bergman, Jeong Joon Park, Axel Levy, Miika Aittala, Shalini De Mello, Tero Karras, Gordon Wetzstein
We present a diffusion-based model for 3D-aware generative novel view synthesis from as few as a single input image.
Compositional 3D Scene Generation using Locally Conditioned Diffusion
no code implementations • 21 Mar 2023 • Ryan Po, Gordon Wetzstein
Designing complex 3D scenes has been a tedious, manual process requiring domain expertise.
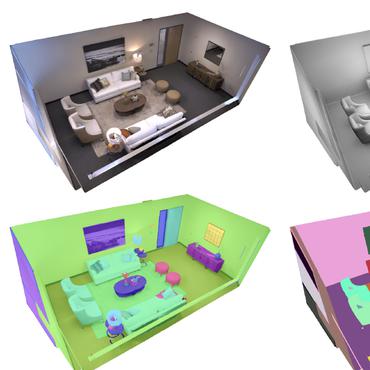
CC3D: Layout-Conditioned Generation of Compositional 3D Scenes
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Sherwin Bahmani, Jeong Joon Park, Despoina Paschalidou, Xingguang Yan, Gordon Wetzstein, Leonidas Guibas, Andrea Tagliasacchi
In this work, we introduce CC3D, a conditional generative model that synthesizes complex 3D scenes conditioned on 2D semantic scene layouts, trained using single-view images.
DehazeNeRF: Multiple Image Haze Removal and 3D Shape Reconstruction using Neural Radiance Fields
no code implementations • 20 Mar 2023 • Wei-Ting Chen, Wang Yifan, Sy-Yen Kuo, Gordon Wetzstein
Neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance for 3D computer vision tasks, including novel view synthesis and 3D shape reconstruction.
MELON: NeRF with Unposed Images in SO(3)
no code implementations • 14 Mar 2023 • Axel Levy, Mark Matthews, Matan Sela, Gordon Wetzstein, Dmitry Lagun
Neural radiance fields enable novel-view synthesis and scene reconstruction with photorealistic quality from a few images, but require known and accurate camera poses.
Diffusion in the Dark: A Diffusion Model for Low-Light Text Recognition
no code implementations • 7 Mar 2023 • Cindy M. Nguyen, Eric R. Chan, Alexander W. Bergman, Gordon Wetzstein
Capturing images is a key part of automation for high-level tasks such as scene text recognition.
PaletteNeRF: Palette-based Appearance Editing of Neural Radiance Fields
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Zhengfei Kuang, Fujun Luan, Sai Bi, Zhixin Shu, Gordon Wetzstein, Kalyan Sunkavalli
Recent advances in neural radiance fields have enabled the high-fidelity 3D reconstruction of complex scenes for novel view synthesis.
PointAvatar: Deformable Point-based Head Avatars from Videos
1 code implementation • CVPR 2023 • Yufeng Zheng, Wang Yifan, Gordon Wetzstein, Michael J. Black, Otmar Hilliges
The ability to create realistic, animatable and relightable head avatars from casual video sequences would open up wide ranging applications in communication and entertainment.
ALTO: Alternating Latent Topologies for Implicit 3D Reconstruction
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Zhen Wang, Shijie Zhou, Jeong Joon Park, Despoina Paschalidou, Suya You, Gordon Wetzstein, Leonidas Guibas, Achuta Kadambi
One school of thought is to encode a latent vector for each point (point latents).
3D Neural Field Generation using Triplane Diffusion
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • J. Ryan Shue, Eric Ryan Chan, Ryan Po, Zachary Ankner, Jiajun Wu, Gordon Wetzstein
Diffusion models have emerged as the state-of-the-art for image generation, among other tasks.
SinGRAF: Learning a 3D Generative Radiance Field for a Single Scene
no code implementations • CVPR 2023 • Minjung Son, Jeong Joon Park, Leonidas Guibas, Gordon Wetzstein
Generative models have shown great promise in synthesizing photorealistic 3D objects, but they require large amounts of training data.
DiffDreamer: Towards Consistent Unsupervised Single-view Scene Extrapolation with Conditional Diffusion Models
no code implementations • ICCV 2023 • Shengqu Cai, Eric Ryan Chan, Songyou Peng, Mohamad Shahbazi, Anton Obukhov, Luc van Gool, Gordon Wetzstein
Scene extrapolation -- the idea of generating novel views by flying into a given image -- is a promising, yet challenging task.
 Ranked #1 on
Perpetual View Generation
on LHQ
Ranked #1 on
Perpetual View Generation
on LHQ
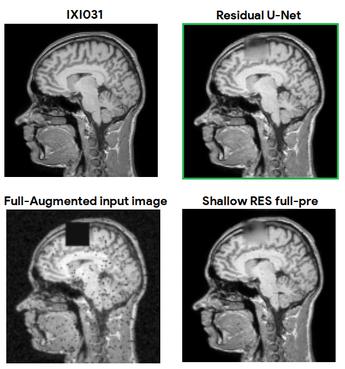
Scale-Agnostic Super-Resolution in MRI using Feature-Based Coordinate Networks
no code implementations • 17 Oct 2022 • Dave Van Veen, Rogier van der Sluijs, Batu Ozturkler, Arjun Desai, Christian Bluethgen, Robert D. Boutin, Marc H. Willis, Gordon Wetzstein, David Lindell, Shreyas Vasanawala, John Pauly, Akshay S. Chaudhari
We propose using a coordinate network decoder for the task of super-resolution in MRI.
Amortized Inference for Heterogeneous Reconstruction in Cryo-EM
no code implementations • 13 Oct 2022 • Axel Levy, Gordon Wetzstein, Julien Martel, Frederic Poitevin, Ellen D. Zhong
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is an imaging modality that provides unique insights into the dynamics of proteins and other building blocks of life.
Heterogeneous reconstruction of deformable atomic models in Cryo-EM
no code implementations • 29 Sep 2022 • Youssef Nashed, Ariana Peck, Julien Martel, Axel Levy, Bongjin Koo, Gordon Wetzstein, Nina Miolane, Daniel Ratner, Frédéric Poitevin
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) provides a unique opportunity to study the structural heterogeneity of biomolecules.
NeuForm: Adaptive Overfitting for Neural Shape Editing
no code implementations • 18 Jul 2022 • Connor Z. Lin, Niloy J. Mitra, Gordon Wetzstein, Leonidas Guibas, Paul Guerrero
Neural representations are popular for representing shapes, as they can be learned form sensor data and used for data cleanup, model completion, shape editing, and shape synthesis.
3D-Aware Video Generation
1 code implementation • 29 Jun 2022 • Sherwin Bahmani, Jeong Joon Park, Despoina Paschalidou, Hao Tang, Gordon Wetzstein, Leonidas Guibas, Luc van Gool, Radu Timofte
Generative models have emerged as an essential building block for many image synthesis and editing tasks.
Generative Neural Articulated Radiance Fields
no code implementations • 28 Jun 2022 • Alexander W. Bergman, Petr Kellnhofer, Wang Yifan, Eric R. Chan, David B. Lindell, Gordon Wetzstein
Unsupervised learning of 3D-aware generative adversarial networks (GANs) using only collections of single-view 2D photographs has very recently made much progress.
Learning to Solve PDE-constrained Inverse Problems with Graph Networks
no code implementations • 1 Jun 2022 • Qingqing Zhao, David B. Lindell, Gordon Wetzstein
Given a sparse set of measurements, we are interested in recovering the initial condition or parameters of the PDE.
Time-multiplexed Neural Holography: A flexible framework for holographic near-eye displays with fast heavily-quantized spatial light modulators
no code implementations • 5 May 2022 • Suyeon Choi, Manu Gopakumar, YiFan, Peng, Jonghyun Kim, Matthew O'Toole, Gordon Wetzstein
Holographic near-eye displays offer unprecedented capabilities for virtual and augmented reality systems, including perceptually important focus cues.
Learning Spatially Varying Pixel Exposures for Motion Deblurring
1 code implementation • 14 Apr 2022 • Cindy M. Nguyen, Julien N. P. Martel, Gordon Wetzstein
Computationally removing the motion blur introduced by camera shake or object motion in a captured image remains a challenging task in computational photography.
3D GAN Inversion for Controllable Portrait Image Animation
no code implementations • 25 Mar 2022 • Connor Z. Lin, David B. Lindell, Eric R. Chan, Gordon Wetzstein
Portrait image animation enables the post-capture adjustment of these attributes from a single image while maintaining a photorealistic reconstruction of the subject's likeness or identity.
CryoAI: Amortized Inference of Poses for Ab Initio Reconstruction of 3D Molecular Volumes from Real Cryo-EM Images
1 code implementation • 15 Mar 2022 • Axel Levy, Frédéric Poitevin, Julien Martel, Youssef Nashed, Ariana Peck, Nina Miolane, Daniel Ratner, Mike Dunne, Gordon Wetzstein
We introduce cryoAI, an ab initio reconstruction algorithm for homogeneous conformations that uses direct gradient-based optimization of particle poses and the electron scattering potential from single-particle cryo-EM data.
Efficient Geometry-aware 3D Generative Adversarial Networks
2 code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Eric R. Chan, Connor Z. Lin, Matthew A. Chan, Koki Nagano, Boxiao Pan, Shalini De Mello, Orazio Gallo, Leonidas Guibas, Jonathan Tremblay, Sameh Khamis, Tero Karras, Gordon Wetzstein
Unsupervised generation of high-quality multi-view-consistent images and 3D shapes using only collections of single-view 2D photographs has been a long-standing challenge.
BACON: Band-limited Coordinate Networks for Multiscale Scene Representation
1 code implementation • CVPR 2022 • David B. Lindell, Dave Van Veen, Jeong Joon Park, Gordon Wetzstein
These networks are trained to map continuous input coordinates to the value of a signal at each point.
MantissaCam: Learning Snapshot High-dynamic-range Imaging with Perceptually-based In-pixel Irradiance Encoding
no code implementations • 9 Dec 2021 • Haley M. So, Julien N. P. Martel, Piotr Dudek, Gordon Wetzstein
We demonstrate the efficacy of our method in simulation and show benefits of our algorithm on modulo images captured with a prototype implemented with a programmable sensor.
Advances in Neural Rendering
1 code implementation • 10 Nov 2021 • Ayush Tewari, Justus Thies, Ben Mildenhall, Pratul Srinivasan, Edgar Tretschk, Yifan Wang, Christoph Lassner, Vincent Sitzmann, Ricardo Martin-Brualla, Stephen Lombardi, Tomas Simon, Christian Theobalt, Matthias Niessner, Jonathan T. Barron, Gordon Wetzstein, Michael Zollhoefer, Vladislav Golyanik
The reconstruction of such a scene representation from observations using differentiable rendering losses is known as inverse graphics or inverse rendering.
Fast Training of Neural Lumigraph Representations using Meta Learning
no code implementations • NeurIPS 2021 • Alexander W. Bergman, Petr Kellnhofer, Gordon Wetzstein
Inspired by neural variants of image-based rendering, we develop a new neural rendering approach with the goal of quickly learning a high-quality representation which can also be rendered in real-time.
ACORN: Adaptive Coordinate Networks for Neural Scene Representation
1 code implementation • 6 May 2021 • Julien N. P. Martel, David B. Lindell, Connor Z. Lin, Eric R. Chan, Marco Monteiro, Gordon Wetzstein
Here, we introduce a new hybrid implicit-explicit network architecture and training strategy that adaptively allocates resources during training and inference based on the local complexity of a signal of interest.
Time-Multiplexed Coded Aperture Imaging: Learned Coded Aperture and Pixel Exposures for Compressive Imaging Systems
no code implementations • ICCV 2021 • Edwin Vargas, Julien N. P. Martel, Gordon Wetzstein, Henry Arguello
Compressive imaging using coded apertures (CA) is a powerful technique that can be used to recover depth, light fields, hyperspectral images and other quantities from a single snapshot.
ScanGAN360: A Generative Model of Realistic Scanpaths for 360$^{\circ}$ Images
no code implementations • 25 Mar 2021 • Daniel Martin, Ana Serrano, Alexander W. Bergman, Gordon Wetzstein, Belen Masia
Generative adversarial approaches could alleviate this challenge by generating a large number of possible scanpaths for unseen images.
Neural Lumigraph Rendering
1 code implementation • CVPR 2021 • Petr Kellnhofer, Lars Jebe, Andrew Jones, Ryan Spicer, Kari Pulli, Gordon Wetzstein
Novel view synthesis is a challenging and ill-posed inverse rendering problem.
AutoInt: Automatic Integration for Fast Neural Volume Rendering
1 code implementation • CVPR 2021 • David B. Lindell, Julien N. P. Martel, Gordon Wetzstein
For training, we instantiate the computational graph corresponding to the derivative of the network.
pi-GAN: Periodic Implicit Generative Adversarial Networks for 3D-Aware Image Synthesis
3 code implementations • CVPR 2021 • Eric R. Chan, Marco Monteiro, Petr Kellnhofer, Jiajun Wu, Gordon Wetzstein
We have witnessed rapid progress on 3D-aware image synthesis, leveraging recent advances in generative visual models and neural rendering.
 Ranked #3 on
Scene Generation
on VizDoom
Ranked #3 on
Scene Generation
on VizDoom
D-VDAMP: Denoising-based Approximate Message Passing for Compressive MRI
1 code implementation • 25 Oct 2020 • Christopher A. Metzler, Gordon Wetzstein
Plug and play (P&P) algorithms iteratively apply highly optimized image denoisers to impose priors and solve computational image reconstruction problems, to great effect.
SUREMap: Predicting Uncertainty in CNN-based Image Reconstruction Using Stein's Unbiased Risk Estimate
1 code implementation • 25 Oct 2020 • Ruangrawee Kitichotkul, Christopher A. Metzler, Frank Ong, Gordon Wetzstein
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) have emerged as a powerful tool for solving computational imaging reconstruction problems.
Single-shot Hyperspectral-Depth Imaging with Learned Diffractive Optics
no code implementations • ICCV 2021 • Seung-Hwan Baek, Hayato Ikoma, Daniel S. Jeon, Yuqi Li, Wolfgang Heidrich, Gordon Wetzstein, Min H. Kim
Imaging depth and spectrum have been extensively studied in isolation from each other for decades.
MetaSDF: Meta-learning Signed Distance Functions
2 code implementations • NeurIPS 2020 • Vincent Sitzmann, Eric R. Chan, Richard Tucker, Noah Snavely, Gordon Wetzstein
Neural implicit shape representations are an emerging paradigm that offers many potential benefits over conventional discrete representations, including memory efficiency at a high spatial resolution.
Implicit Neural Representations with Periodic Activation Functions
24 code implementations • NeurIPS 2020 • Vincent Sitzmann, Julien N. P. Martel, Alexander W. Bergman, David B. Lindell, Gordon Wetzstein
However, current network architectures for such implicit neural representations are incapable of modeling signals with fine detail, and fail to represent a signal's spatial and temporal derivatives, despite the fact that these are essential to many physical signals defined implicitly as the solution to partial differential equations.
State of the Art on Neural Rendering
no code implementations • 8 Apr 2020 • Ayush Tewari, Ohad Fried, Justus Thies, Vincent Sitzmann, Stephen Lombardi, Kalyan Sunkavalli, Ricardo Martin-Brualla, Tomas Simon, Jason Saragih, Matthias Nießner, Rohit Pandey, Sean Fanello, Gordon Wetzstein, Jun-Yan Zhu, Christian Theobalt, Maneesh Agrawala, Eli Shechtman, Dan B. Goldman, Michael Zollhöfer
Neural rendering is a new and rapidly emerging field that combines generative machine learning techniques with physical knowledge from computer graphics, e. g., by the integration of differentiable rendering into network training.
Event Based, Near Eye Gaze Tracking Beyond 10,000Hz
1 code implementation • 7 Apr 2020 • Anastasios N. Angelopoulos, Julien N. P. Martel, Amit P. S. Kohli, Jorg Conradt, Gordon Wetzstein
The cameras in modern gaze-tracking systems suffer from fundamental bandwidth and power limitations, constraining data acquisition speed to 300 Hz realistically.
Semantic Implicit Neural Scene Representations With Semi-Supervised Training
no code implementations • 28 Mar 2020 • Amit Kohli, Vincent Sitzmann, Gordon Wetzstein
The recent success of implicit neural scene representations has presented a viable new method for how we capture and store 3D scenes.
Deep S$^3$PR: Simultaneous Source Separation and Phase Retrieval Using Deep Generative Models
1 code implementation • 14 Feb 2020 • Christopher A. Metzler, Gordon Wetzstein
This paper introduces and solves the simultaneous source separation and phase retrieval (S$^3$PR) problem.
Keyhole Imaging: Non-Line-of-Sight Imaging and Tracking of Moving Objects Along a Single Optical Path
no code implementations • 13 Dec 2019 • Christopher A. Metzler, David B. Lindell, Gordon Wetzstein
Non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging and tracking is an emerging technology that allows the shape or position of objects around corners or behind diffusers to be recovered from transient, time-of-flight measurements.
Deep Optics for Single-shot High-dynamic-range Imaging
no code implementations • CVPR 2020 • Christopher A. Metzler, Hayato Ikoma, Yifan Peng, Gordon Wetzstein
High-dynamic-range (HDR) imaging is crucial for many computer graphics and vision applications.
Scene Representation Networks: Continuous 3D-Structure-Aware Neural Scene Representations
1 code implementation • NeurIPS 2019 • Vincent Sitzmann, Michael Zollhöfer, Gordon Wetzstein
Unsupervised learning with generative models has the potential of discovering rich representations of 3D scenes.
Deep Optics for Monocular Depth Estimation and 3D Object Detection
no code implementations • ICCV 2019 • Julie Chang, Gordon Wetzstein
In addition, we train object detection networks on the KITTI dataset and show that the lens optimized for depth estimation also results in improved 3D object detection performance.
 Ranked #11 on
Depth Estimation
on NYU-Depth V2
Ranked #11 on
Depth Estimation
on NYU-Depth V2
LiFF: Light Field Features in Scale and Depth
1 code implementation • CVPR 2019 • Donald G. Dansereau, Bernd Girod, Gordon Wetzstein
Feature detectors and descriptors are key low-level vision tools that many higher-level tasks build on.
DeepVoxels: Learning Persistent 3D Feature Embeddings
1 code implementation • CVPR 2019 • Vincent Sitzmann, Justus Thies, Felix Heide, Matthias Nießner, Gordon Wetzstein, Michael Zollhöfer
In this work, we address the lack of 3D understanding of generative neural networks by introducing a persistent 3D feature embedding for view synthesis.
Convolutional Sparse Coding for High Dynamic Range Imaging
no code implementations • 13 Jun 2018 • Ana Serrano, Felix Heide, Diego Gutierrez, Gordon Wetzstein, Belen Masia
Current HDR acquisition techniques are based on either (i) fusing multibracketed, low dynamic range (LDR) images, (ii) modifying existing hardware and capturing different exposures simultaneously with multiple sensors, or (iii) reconstructing a single image with spatially-varying pixel exposures.
Deep End-to-End Time-of-Flight Imaging
no code implementations • CVPR 2018 • Shuochen Su, Felix Heide, Gordon Wetzstein, Wolfgang Heidrich
We present an end-to-end image processing framework for time-of-flight (ToF) cameras.
Non-line-of-sight Imaging with Partial Occluders and Surface Normals
no code implementations • 20 Nov 2017 • Felix Heide, Matthew O'Toole, Kai Zang, David Lindell, Steven Diamond, Gordon Wetzstein
Imaging objects obscured by occluders is a significant challenge for many applications.
Consensus Convolutional Sparse Coding
1 code implementation • ICCV 2017 • Biswarup Choudhury, Robin Swanson, Felix Heide, Gordon Wetzstein, Wolfgang Heidrich
Convolutional sparse coding (CSC) is a promising direction for unsupervised learning in computer vision.
A Wide-Field-Of-View Monocentric Light Field Camera
no code implementations • CVPR 2017 • Donald G. Dansereau, Glenn Schuster, Joseph Ford, Gordon Wetzstein
Finally, we describe a processing toolchain, including a convenient spherical LF parameterization, and demonstrate depth estimation and post-capture refocus for indoor and outdoor panoramas with 15 x 15 x 1600 x 200 pixels (72 MPix) and a 138-degree FOV.
Reconstructing Transient Images From Single-Photon Sensors
no code implementations • CVPR 2017 • Matthew O'Toole, Felix Heide, David B. Lindell, Kai Zang, Steven Diamond, Gordon Wetzstein
Computer vision algorithms build on 2D images or 3D videos that capture dynamic events at the millisecond time scale.
Unrolled Optimization with Deep Priors
2 code implementations • 22 May 2017 • Steven Diamond, Vincent Sitzmann, Felix Heide, Gordon Wetzstein
A broad class of problems at the core of computational imaging, sensing, and low-level computer vision reduces to the inverse problem of extracting latent images that follow a prior distribution, from measurements taken under a known physical image formation model.
Snapshot Difference Imaging using Time-of-Flight Sensors
no code implementations • 19 May 2017 • Clara Callenberg, Felix Heide, Gordon Wetzstein, Matthias Hullin
Computational photography encompasses a diversity of imaging techniques, but one of the core operations performed by many of them is to compute image differences.
Dirty Pixels: Towards End-to-End Image Processing and Perception
1 code implementation • 23 Jan 2017 • Steven Diamond, Vincent Sitzmann, Frank Julca-Aguilar, Stephen Boyd, Gordon Wetzstein, Felix Heide
As such, conventional imaging involves processing the RAW sensor measurements in a sequential pipeline of steps, such as demosaicking, denoising, deblurring, tone-mapping and compression.
How do people explore virtual environments?
no code implementations • 13 Dec 2016 • Vincent Sitzmann, Ana Serrano, Amy Pavel, Maneesh Agrawala, Diego Gutierrez, Belen Masia, Gordon Wetzstein
Understanding how people explore immersive virtual environments is crucial for many applications, such as designing virtual reality (VR) content, developing new compression algorithms, or learning computational models of saliency or visual attention.
Variable Aperture Light Field Photography: Overcoming the Diffraction-Limited Spatio-Angular Resolution Tradeoff
no code implementations • CVPR 2016 • Julie Chang, Isaac Kauvar, Xuemei Hu, Gordon Wetzstein
Light fields have many applications in machine vision, consumer photography, robotics, and microscopy.
Fast and Flexible Convolutional Sparse Coding
no code implementations • CVPR 2015 • Felix Heide, Wolfgang Heidrich, Gordon Wetzstein
Convolutional sparse coding (CSC) has become an increasingly important tool in machine learning and computer vision.
Transparent Object Reconstruction via Coded Transport of Intensity
no code implementations • CVPR 2014 • Chenguang Ma, Xing Lin, Jinli Suo, Qionghai Dai, Gordon Wetzstein
Capturing and understanding visual signals is one of the core interests of computer vision.