Search Results for author: Yi-Hsuan Tsai
Found 64 papers, 36 papers with code
Colorization of Depth Map via Disentanglement
1 code implementation • ECCV 2020 • Chung-Sheng Lai, Zunzhi You, Ching-Chun Huang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu
Vision perception is one of the most important components for a computer or robot to understand the surrounding scene and achieve autonomous applications.
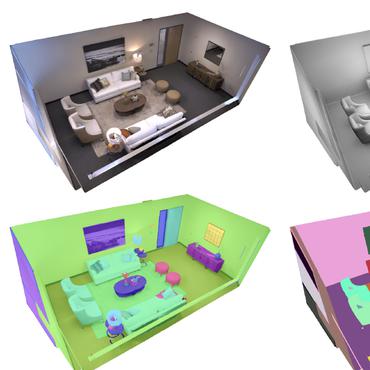
Gaga: Group Any Gaussians via 3D-aware Memory Bank
no code implementations • 11 Apr 2024 • Weijie Lyu, Xueting Li, Abhijit Kundu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
We introduce Gaga, a framework that reconstructs and segments open-world 3D scenes by leveraging inconsistent 2D masks predicted by zero-shot segmentation models.
PTT: Point-Trajectory Transformer for Efficient Temporal 3D Object Detection
1 code implementation • 13 Dec 2023 • Kuan-Chih Huang, Weijie Lyu, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
Recent temporal LiDAR-based 3D object detectors achieve promising performance based on the two-stage proposal-based approach.
Weakly Supervised 3D Object Detection via Multi-Level Visual Guidance
no code implementations • 12 Dec 2023 • Kuan-Chih Huang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Finally, the training-level constraint is utilized by producing accurate and consistent 3D pseudo-labels that align with the visual data.
Diffusion-SS3D: Diffusion Model for Semi-supervised 3D Object Detection
1 code implementation • NeurIPS 2023 • Cheng-Ju Ho, Chen-Hsuan Tai, Yen-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
Semi-supervised object detection is crucial for 3D scene understanding, efficiently addressing the limitation of acquiring large-scale 3D bounding box annotations.
Action-slot: Visual Action-centric Representations for Multi-label Atomic Activity Recognition in Traffic Scenes
no code implementations • 29 Nov 2023 • Chi-Hsi Kung, Shu-Wei Lu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Yi-Ting Chen
In this paper, we introduce Action-slot, a slot attention-based approach that learns visual action-centric representations, capturing both motion and contextual information.
Text-Driven Image Editing via Learnable Regions
1 code implementation • 28 Nov 2023 • Yuanze Lin, Yi-Wen Chen, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Lu Jiang, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Language has emerged as a natural interface for image editing.
Editing 3D Scenes via Text Prompts without Retraining
no code implementations • 10 Sep 2023 • Shuangkang Fang, Yufeng Wang, Yi Yang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wenrui Ding, Shuchang Zhou, Ming-Hsuan Yang
To tackle these issues, we introduce a text-driven editing method, termed DN2N, which allows for the direct acquisition of a NeRF model with universal editing capabilities, eliminating the requirement for retraining.
Delving into Motion-Aware Matching for Monocular 3D Object Tracking
1 code implementation • ICCV 2023 • Kuan-Chih Huang, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
In this paper, we find that the motion cue of objects along different time frames is critical in 3D multi-object tracking, which is less explored in existing monocular-based approaches.
Multimodal Prompting with Missing Modalities for Visual Recognition
1 code implementation • CVPR 2023 • Yi-Lun Lee, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu, Chen-Yu Lee
In this paper, we tackle two challenges in multimodal learning for visual recognition: 1) when missing-modality occurs either during training or testing in real-world situations; and 2) when the computation resources are not available to finetune on heavy transformer models.
Learning Object-level Point Augmentor for Semi-supervised 3D Object Detection
1 code implementation • 19 Dec 2022 • Cheng-Ju Ho, Chen-Hsuan Tai, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Yen-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsuan Yang
In this work, we propose an object-level point augmentor (OPA) that performs local transformations for semi-supervised 3D object detection.
Learning Phase Mask for Privacy-Preserving Passive Depth Estimation
no code implementations • European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2022 • Zaid Tasneem, Giovanni Milione, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Xiang Yu, Ashok Veeraraghavan, Manmohan Chandraker, Francesco Pittaluga
With over a billion sold each year, cameras are not only becoming ubiquitous and omnipresent, but are driving progress in a wide range of applications such as augmented/virtual reality, robotics, surveillance, security, autonomous navigation and many others.
360-MLC: Multi-view Layout Consistency for Self-training and Hyper-parameter Tuning
1 code implementation • 24 Oct 2022 • Bolivar Solarte, Chin-Hsuan Wu, Yueh-Cheng Liu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Min Sun
In addition, since ground truth annotations are not available during training nor in testing, we leverage the entropy information in multiple layout estimations as a quantitative metric to measure the geometry consistency of the scene, allowing us to evaluate any layout estimator for hyper-parameter tuning, including model selection without ground truth annotations.
3D-PL: Domain Adaptive Depth Estimation with 3D-aware Pseudo-Labeling
1 code implementation • 19 Sep 2022 • Yu-Ting Yen, Chia-Ni Lu, Wei-Chen Chiu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
In this paper, we develop a domain adaptation framework via generating reliable pseudo ground truths of depth from real data to provide direct supervisions.
BiFuse++: Self-supervised and Efficient Bi-projection Fusion for 360 Depth Estimation
1 code implementation • 7 Sep 2022 • Fu-En Wang, Yu-Hsuan Yeh, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu, Min Sun
Thus, state-of-the-art frameworks for monocular 360 depth estimation such as bi-projection fusion in BiFuse are proposed.
 Ranked #12 on
Depth Estimation
on Stanford2D3D Panoramic
Ranked #12 on
Depth Estimation
on Stanford2D3D Panoramic
MM-TTA: Multi-Modal Test-Time Adaptation for 3D Semantic Segmentation
no code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Inkyu Shin, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Bingbing Zhuang, Samuel Schulter, Buyu Liu, Sparsh Garg, In So Kweon, Kuk-Jin Yoon
In this paper, we propose and explore a new multi-modal extension of test-time adaptation for 3D semantic segmentation.
On Generalizing Beyond Domains in Cross-Domain Continual Learning
no code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Christian Simon, Masoud Faraki, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Xiang Yu, Samuel Schulter, Yumin Suh, Mehrtash Harandi, Manmohan Chandraker
Humans have the ability to accumulate knowledge of new tasks in varying conditions, but deep neural networks often suffer from catastrophic forgetting of previously learned knowledge after learning a new task.
Learning Semantic Segmentation from Multiple Datasets with Label Shifts
no code implementations • 28 Feb 2022 • Dongwan Kim, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Yumin Suh, Masoud Faraki, Sparsh Garg, Manmohan Chandraker, Bohyung Han
First, a gradient conflict in training due to mismatched label spaces is identified and a class-independent binary cross-entropy loss is proposed to alleviate such label conflicts.
Self-Supervised Feature Learning from Partial Point Clouds via Pose Disentanglement
no code implementations • 9 Jan 2022 • Meng-Shiun Tsai, Pei-Ze Chiang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu
Self-supervised learning on point clouds has gained a lot of attention recently, since it addresses the label-efficiency and domain-gap problems on point cloud tasks.
360-DFPE: Leveraging Monocular 360-Layouts for Direct Floor Plan Estimation
1 code implementation • 12 Dec 2021 • Bolivar Solarte, Yueh-Cheng Liu, Chin-Hsuan Wu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Min Sun
We present 360-DFPE, a sequential floor plan estimation method that directly takes 360-images as input without relying on active sensors or 3D information.
Semi-supervised Multi-task Learning for Semantics and Depth
no code implementations • 14 Oct 2021 • Yufeng Wang, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chih Hung, Wenrui Ding, Shuo Liu, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Multi-Task Learning (MTL) aims to enhance the model generalization by sharing representations between related tasks for better performance.
Learning to Learn across Diverse Data Biases in Deep Face Recognition
no code implementations • CVPR 2022 • Chang Liu, Xiang Yu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ramin Moslemi, Masoud Faraki, Manmohan Chandraker, Yun Fu
Convolutional Neural Networks have achieved remarkable success in face recognition, in part due to the abundant availability of data.
Learning Cross-modal Contrastive Features for Video Domain Adaptation
no code implementations • ICCV 2021 • Donghyun Kim, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Bingbing Zhuang, Xiang Yu, Stan Sclaroff, Kate Saenko, Manmohan Chandraker
Learning transferable and domain adaptive feature representations from videos is important for video-relevant tasks such as action recognition.
Towards Interpretable Deep Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation
1 code implementation • ICCV 2021 • Zunzhi You, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu, Guanbin Li
Based on our observations, we quantify the interpretability of a deep MDE network by the depth selectivity of its hidden units.
End-to-end Multi-modal Video Temporal Grounding
1 code implementation • NeurIPS 2021 • Yi-Wen Chen, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Specifically, we adopt RGB images for appearance, optical flow for motion, and depth maps for image structure.
LED2-Net: Monocular 360deg Layout Estimation via Differentiable Depth Rendering
no code implementations • CVPR 2021 • Fu-En Wang, Yu-Hsuan Yeh, Min Sun, Wei-Chen Chiu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
Although significant progress has been made in room layout estimation, most methods aim to reduce the loss in the 2D pixel coordinate rather than exploiting the room structure in the 3D space.
Robust 360-8PA: Redesigning The Normalized 8-point Algorithm for 360-FoV Images
1 code implementation • 22 Apr 2021 • Bolivar Solarte, Chin-Hsuan Wu, Kuan-Wei Lu, Min Sun, Wei-Chen Chiu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
This paper presents a novel preconditioning strategy for the classic 8-point algorithm (8-PA) for estimating an essential matrix from 360-FoV images (i. e., equirectangular images) in spherical projection.
Understanding Synonymous Referring Expressions via Contrastive Features
1 code implementation • 20 Apr 2021 • Yi-Wen Chen, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
While prior work usually treats each sentence and attends it to an object separately, we focus on learning a referring expression comprehension model that considers the property in synonymous sentences.
LED2-Net: Monocular 360 Layout Estimation via Differentiable Depth Rendering
1 code implementation • 1 Apr 2021 • Fu-En Wang, Yu-Hsuan Yeh, Min Sun, Wei-Chen Chiu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
Although significant progress has been made in room layout estimation, most methods aim to reduce the loss in the 2D pixel coordinate rather than exploiting the room structure in the 3D space.
 3D Room Layouts From A Single RGB Panorama
3D Room Layouts From A Single RGB Panorama
 Depth Estimation
+2
Depth Estimation
+2
Cross-Domain Similarity Learning for Face Recognition in Unseen Domains
no code implementations • CVPR 2021 • Masoud Faraki, Xiang Yu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Yumin Suh, Manmohan Chandraker
Intuitively, it discriminatively correlates explicit metrics derived from one domain, with triplet samples from another domain in a unified loss function to be minimized within a network, which leads to better alignment of the training domains.
Dual-Stream Fusion Network for Spatiotemporal Video Super-Resolution
1 code implementation • Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2021 • Min-Yuan Tseng, Yen-Chung Chen, Yi-Lun Lee, Wei-Sheng Lai, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu
Our method is based on an important observation that: even the direct cascade of prior research in spatial and temporal super-resolution can achieve the spatiotemporal upsampling, changing orders for combining them would lead to results with a complementary property.
Voting-based Approaches For Differentially Private Federated Learning
no code implementations • 9 Oct 2020 • Yuqing Zhu, Xiang Yu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Francesco Pittaluga, Masoud Faraki, Manmohan Chandraker, Yu-Xiang Wang
Differentially Private Federated Learning (DPFL) is an emerging field with many applications.
Every Pixel Matters: Center-aware Feature Alignment for Domain Adaptive Object Detector
1 code implementation • ECCV 2020 • Cheng-Chun Hsu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Yen-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsuan Yang
A domain adaptive object detector aims to adapt itself to unseen domains that may contain variations of object appearance, viewpoints or backgrounds.
Object Detection with a Unified Label Space from Multiple Datasets
no code implementations • ECCV 2020 • Xiangyun Zhao, Samuel Schulter, Gaurav Sharma, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Manmohan Chandraker, Ying Wu
To address this challenge, we design a framework which works with such partial annotations, and we exploit a pseudo labeling approach that we adapt for our specific case.
Learning to Caricature via Semantic Shape Transform
1 code implementation • 12 Aug 2020 • Wenqing Chu, Wei-Chih Hung, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Yu-Ting Chang, Yijun Li, Deng Cai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Caricature is an artistic drawing created to abstract or exaggerate facial features of a person.
Mixup-CAM: Weakly-supervised Semantic Segmentation via Uncertainty Regularization
no code implementations • 3 Aug 2020 • Yu-Ting Chang, Qiaosong Wang, Wei-Chih Hung, Robinson Piramuthu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Obtaining object response maps is one important step to achieve weakly-supervised semantic segmentation using image-level labels.
Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation via Sub-category Exploration
1 code implementation • CVPR 2020 • Yu-Ting Chang, Qiaosong Wang, Wei-Chih Hung, Robinson Piramuthu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Existing weakly-supervised semantic segmentation methods using image-level annotations typically rely on initial responses to locate object regions.
Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation Using Weak Labels
no code implementations • ECCV 2020 • Sujoy Paul, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Samuel Schulter, Amit K. Roy-Chowdhury, Manmohan Chandraker
In this work, we propose a novel framework for domain adaptation in semantic segmentation with image-level weak labels in the target domain.
Regularizing Meta-Learning via Gradient Dropout
1 code implementation • 13 Apr 2020 • Hung-Yu Tseng, Yi-Wen Chen, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Sifei Liu, Yen-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsuan Yang
With the growing attention on learning-to-learn new tasks using only a few examples, meta-learning has been widely used in numerous problems such as few-shot classification, reinforcement learning, and domain generalization.
LayoutMP3D: Layout Annotation of Matterport3D
1 code implementation • 30 Mar 2020 • Fu-En Wang, Yu-Hsuan Yeh, Min Sun, Wei-Chen Chiu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai
Inferring the information of 3D layout from a single equirectangular panorama is crucial for numerous applications of virtual reality or robotics (e. g., scene understanding and navigation).
Adversarial Learning of Privacy-Preserving and Task-Oriented Representations
no code implementations • 22 Nov 2019 • Taihong Xiao, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Kihyuk Sohn, Manmohan Chandraker, Ming-Hsuan Yang
For instance, there could be a potential privacy risk of machine learning systems via the model inversion attack, whose goal is to reconstruct the input data from the latent representation of deep networks.
360SD-Net: 360° Stereo Depth Estimation with Learnable Cost Volume
1 code implementation • 11 Nov 2019 • Ning-Hsu Wang, Bolivar Solarte, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu, Min Sun
Recently, end-to-end trainable deep neural networks have significantly improved stereo depth estimation for perspective images.
Progressive Domain Adaptation for Object Detection
1 code implementation • 24 Oct 2019 • Han-Kai Hsu, Chun-Han Yao, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chih Hung, Hung-Yu Tseng, Maneesh Singh, Ming-Hsuan Yang
This intermediate domain is constructed by translating the source images to mimic the ones in the target domain.
Referring Expression Object Segmentation with Caption-Aware Consistency
1 code implementation • 10 Oct 2019 • Yi-Wen Chen, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Tiantian Wang, Yen-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsuan Yang
To this end, we propose an end-to-end trainable comprehension network that consists of the language and visual encoders to extract feature representations from both domains.
 Ranked #19 on
Referring Expression Segmentation
on RefCOCO testB
Ranked #19 on
Referring Expression Segmentation
on RefCOCO testB
Adaptation Across Extreme Variations using Unlabeled Domain Bridges
no code implementations • 5 Jun 2019 • Shuyang Dai, Kihyuk Sohn, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Lawrence Carin, Manmohan Chandraker
We tackle an unsupervised domain adaptation problem for which the domain discrepancy between labeled source and unlabeled target domains is large, due to many factors of inter and intra-domain variation.
Bridging Stereo Matching and Optical Flow via Spatiotemporal Correspondence
1 code implementation • CVPR 2019 • Hsueh-Ying Lai, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu
In this paper, we propose a single and principled network to jointly learn spatiotemporal correspondence for stereo matching and flow estimation, with a newly designed geometric connection as the unsupervised signal for temporally adjacent stereo pairs.
Weakly-supervised Caricature Face Parsing through Domain Adaptation
1 code implementation • 13 May 2019 • Wenqing Chu, Wei-Chih Hung, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Deng Cai, Ming-Hsuan Yang
However, current state-of-the-art face parsing methods require large amounts of labeled data on the pixel-level and such process for caricature is tedious and labor-intensive.
Domain Adaptation for Structured Output via Disentangled Patch Representations
no code implementations • ICLR 2019 • Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Kihyuk Sohn, Samuel Schulter, Manmohan Chandraker
To this end, we propose to learn discriminative feature representations of patches based on label histograms in the source domain, through the construction of a disentangled space.
Active Adversarial Domain Adaptation
no code implementations • 16 Apr 2019 • Jong-Chyi Su, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Kihyuk Sohn, Buyu Liu, Subhransu Maji, Manmohan Chandraker
Our approach, active adversarial domain adaptation (AADA), explores a duality between two related problems: adversarial domain alignment and importance sampling for adapting models across domains.
3D LiDAR and Stereo Fusion using Stereo Matching Network with Conditional Cost Volume Normalization
1 code implementation • 5 Apr 2019 • Tsun-Hsuan Wang, Hou-Ning Hu, Chieh Hubert Lin, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu, Min Sun
The complementary characteristics of active and passive depth sensing techniques motivate the fusion of the Li-DAR sensor and stereo camera for improved depth perception.
Domain Adaptation for Structured Output via Discriminative Patch Representations
8 code implementations • ICCV 2019 • Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Kihyuk Sohn, Samuel Schulter, Manmohan Chandraker
Predicting structured outputs such as semantic segmentation relies on expensive per-pixel annotations to learn supervised models like convolutional neural networks.
 Ranked #22 on
Image-to-Image Translation
on SYNTHIA-to-Cityscapes
Ranked #22 on
Image-to-Image Translation
on SYNTHIA-to-Cityscapes
Unseen Object Segmentation in Videos via Transferable Representations
no code implementations • 8 Jan 2019 • Yi-Wen Chen, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Chu-Ya Yang, Yen-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsuan Yang
The entire process is decomposed into two tasks: 1) solving a submodular function for selecting object-like segments, and 2) learning a CNN model with a transferable module for adapting seen categories in the source domain to the unseen target video.
Plug-and-Play: Improve Depth Estimation via Sparse Data Propagation
2 code implementations • 20 Dec 2018 • Tsun-Hsuan Wang, Fu-En Wang, Juan-Ting Lin, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu, Min Sun
We propose a novel plug-and-play (PnP) module for improving depth prediction with taking arbitrary patterns of sparse depths as input.
Learning to Adapt Structured Output Space for Semantic Segmentation
12 code implementations • CVPR 2018 • Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chih Hung, Samuel Schulter, Kihyuk Sohn, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Manmohan Chandraker
In this paper, we propose an adversarial learning method for domain adaptation in the context of semantic segmentation.
 Ranked #3 on
Domain Adaptation
on Synscapes-to-Cityscapes
Ranked #3 on
Domain Adaptation
on Synscapes-to-Cityscapes
Adversarial Learning for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
13 code implementations • ICLR 2018 • Wei-Chih Hung, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Yan-Ting Liou, Yen-Yu Lin, Ming-Hsuan Yang
We propose a method for semi-supervised semantic segmentation using an adversarial network.
Learning Video-Story Composition via Recurrent Neural Network
no code implementations • 31 Jan 2018 • Guangyu Zhong, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Sifei Liu, Zhixun Su, Ming-Hsuan Yang
In this paper, we propose a learning-based method to compose a video-story from a group of video clips that describe an activity or experience.
Learning Binary Residual Representations for Domain-specific Video Streaming
no code implementations • 14 Dec 2017 • Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Yu Liu, Deqing Sun, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Jan Kautz
Specifically, we target a streaming setting where the videos to be streamed from a server to a client are all in the same domain and they have to be compressed to a small size for low-latency transmission.
Scene Parsing with Global Context Embedding
1 code implementation • ICCV 2017 • Wei-Chih Hung, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Xiaohui Shen, Zhe Lin, Kalyan Sunkavalli, Xin Lu, Ming-Hsuan Yang
We present a scene parsing method that utilizes global context information based on both the parametric and non- parametric models.
SegFlow: Joint Learning for Video Object Segmentation and Optical Flow
1 code implementation • ICCV 2017 • Jingchun Cheng, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Shengjin Wang, Ming-Hsuan Yang
This paper proposes an end-to-end trainable network, SegFlow, for simultaneously predicting pixel-wise object segmentation and optical flow in videos.
![]() Ranked #67 on
Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
on DAVIS 2016
Ranked #67 on
Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
on DAVIS 2016
Learning to Segment Instances in Videos with Spatial Propagation Network
no code implementations • 14 Sep 2017 • Jingchun Cheng, Sifei Liu, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chih Hung, Shalini De Mello, Jinwei Gu, Jan Kautz, Shengjin Wang, Ming-Hsuan Yang
In addition, we apply a filter on the refined score map that aims to recognize the best connected region using spatial and temporal consistencies in the video.
Deep Image Harmonization
2 code implementations • CVPR 2017 • Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Xiaohui Shen, Zhe Lin, Kalyan Sunkavalli, Xin Lu, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Compositing is one of the most common operations in photo editing.
Video Segmentation via Object Flow
no code implementations • CVPR 2016 • Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Michael J. Black
Video object segmentation is challenging due to fast moving objects, deforming shapes, and cluttered backgrounds.
![]() Ranked #74 on
Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
on DAVIS 2016
(using extra training data)
Ranked #74 on
Semi-Supervised Video Object Segmentation
on DAVIS 2016
(using extra training data)
Adaptive Region Pooling for Object Detection
no code implementations • CVPR 2015 • Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Onur C. Hamsici, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Learning models for object detection is a challenging problem due to the large intra-class variability of objects in appearance, viewpoints, and rigidity.